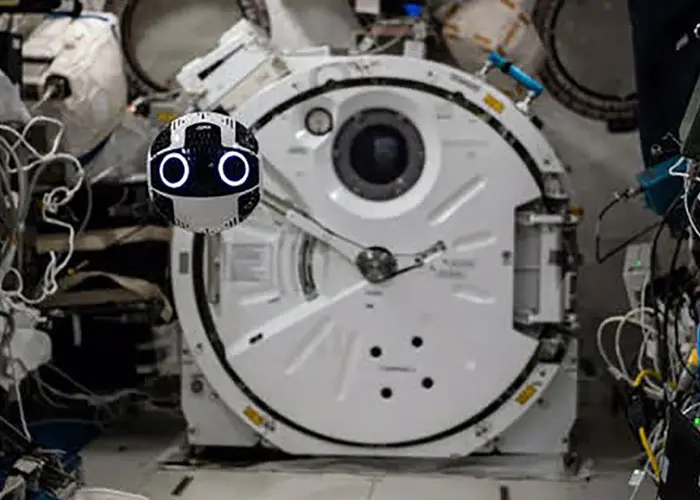
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency has selected an inertial measurement unit (IMU) from Epson’s M-G370 series for use in a mobile camera robot deployed on Kibo, their experimental module on the International Space Station (ISS). The IMU assists in stabilisation control for flight and automated docking for battery charging.
The Internal Ball Camera 2 free-flying camera robot has been undergoing functional verification inside Kibo since June 2023. The camera is an onboard drone robot. It is operated remotely by ground control and can fly around the ISS.
The Internal Ball Camera 2 is designed to automatically depart and return to its docking station for recharging. However, it must navigate in a micro-gravity environment. To do this, it is required to estimate its 3DoF position (X, Y, Z) and 3DoF rotational attitude (roll, pitch, and yaw). The camera estimates its position by fusing Visual Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (VSLAM) and IMU data.
The Epson IMU used in the camera testing is a small, lightweight, yet extremely precise device that helps estimate spatial position and rotational attitude during its flight.
Main features of the IMU include;
- An original crystal gyroscopic sensor for high precision and stability;
- Gyro bias instability 0.8°/√h Angle random walk 0.06-0.03°/√h;
- Compact and lightweight (1″ square and 10 grams); and
- Low power design (3.3 V, 16 mA).





